Ceres
New Planet in the Belt!!! CERES!!!!
This the new planet that was discovered in the Asteroid Belt called Ceres. It is beleived that Ceres may contain water as seen by the fourth image. Ceres is classed as the Fifth Planet in our new ever changing Solar System.
How many planets are there
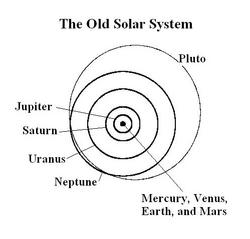
While most people would answer that there are 9 or perhaps 10 planets, a proposal by the International Astronomical Union that will be voted on soon would significantly increase the number of objects that astronomers call planets. The proposal is to call any object that is large enough to make gravity cause it to become round a planet.
How many planets would this make? The nine planets that everyone knows are all round, so they are clearly planets. Ceres, the largest asteroid, is also round and would become a planet (the fifth). The big question, then, is how many new planets are there in the Kuiper belt, a region of rocky/icy bodies beyond Neptune, and the home of Pluto and 2003 UB313 ("the 10th planet").
While we can't see most of the objects in the Kuiper belt well enough to determine whether they are round or not, we can estimate how big an object has to be before it becomes round and therefore how many objects in the Kuiper belt are likely round. In the asteroid belt Ceres, with a diameter of 900 km, is the only object large enough to be round, so somewhere around 900 km is a good cutoff for rocky bodies like asteroids. Kuiper belt objects have a lot of ice in their interiors, though. Ice is not as hard as rock, so it less easily withstands the force of gravity, and it takes less force to make an ice ball round. The best estimate for how big an icy body needs to be to become round comes from looking at icy satellites of the giant planets. The smallest body that is generally round is Saturn's satellite Mimas, which has a diameter of about 400 km. Several satellites which have diameters around 200 km are not round. So somewhere between 200 and 400 km an icy body becomes round. Objects with more ice will become round at smaller sizes while those with less rock might be bigger. We will take 400 km as a reasonable lower limit and assume that anything larger than 400 km in the Kuiper belt is round, and thus a planet.
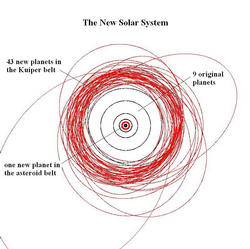
How many objects larger than 400 km are there in the Kuiper belt? We can't answer this question precisely, because we don't know the sizes of more than a handful of Kuiper belt objects (for an explanation why, see the discussion on the size of 2003 UB313), but, again, we can make a reasonable guess. If we assume that the typical small Kuiper belt object reflects 10% of the sunlight that hits its surface we know how bright a 400 km object would be in the Kuiper belt. As of late August 2006, 44 objects this size or larger in the Kuiper belt (including, of course, 2003 UB313 and Pluto), and one (Sedna) in the region beyond the Kuiper belt. In addition our large ongoing Palomar survey has detected approximately 30 more objects of this size which are currently undergoing detailed study.
We have not yet completed our survey of the Kuiper belt. Our best estimate is that a complete survey of the Kuiper belt would more than triple this number.
For now, the number of known objects in the solar system which are likely to be round is 53, with the number jumping to 80 when the objects from our survey are announced, and to more than 200 when the Kuiper belt is fully surveyed.
The large number of new planets in the solar system are very different from the previous 9 planets. Most are so small that they are smaller across than the distance from Los Angeles to San Francisco. They are so small that about 30,000 of them could fit inside the earth.
Who has discovered planets?
Previously, the only official planet discoverers were William Herschel (one planet: Uranus), Le Verrier/Adams (one planet: Neptune), and Tombaugh (one planet: Pluto).
Now the club is much much larger (some planets were discovered by teams which change a bit, in general the team name or the team leader is listed. Sometimes no discoverer is recorded):
- Brown et al.: 15 planets
- Deep Ecliptic Survey: 8 planets
- Near Earth Asteroid Tracking Survey: 4 planets
- Spacewatch: 4 planets
- Jewitt et al.: 3 planets
- Rupenstein, Ferrin, Danzl, Roe, Luu: 1 each
| name | average distance from sun (semimajor axis, AU) | estimated size (km) | |
| Mercury | 0.39 | 4880 | |
| Venus | 0.72 | 12,100 | |
| Earth | 1.0 | 12,700 | |
| Mars | 1.5 | 6780 | |
| Ceres | 2.8 | 950 | |
| Jupiter | 5.2 | 139,800 | |
| Saturn | 9.6 | 116,500 | |
| Uranus | 19.2 | 50,700 | |
| Neptune | 30.0 | 49,200 | |
| 2004TY364 | 38.72 | 540 | |
| 2002KX14 | 39.01 | 560 | |
| 2002XV93 | 39.22 | 430 | |
| 2003VS2 | 39.27 | 610 | |
| 1999TC36 | 39.27 | 440 | |
| 2001QF298 | 39.30 | 490 | |
| Orcus | 39.34 | 1100 | |
| 2003AZ84 | 39.45 | 710 | |
| Pluto | 39.53 | 2300 | |
| Ixion | 39.65 | 980 | |
| Huya | 39.76 | 480 | |
| 2005RN43 | 41.53 | 740 | |
| 1995SM55 | 41.64 | 470 | |
| 2002MS4 | 41.90 | 740 | |
| 2004SB60 | 41.97 | 560 | |
| 2004GV9 | 42.23 | 680 | |
| 2002UX25 | 42.53 | 810 | |
| Varuna | 42.90 | 780 | |
| 2002TX300 | 43.11 | 800 | |
| 1996TO66 | 43.19 | 540 | |
| 2003OP32 | 43.24 | 650 | |
| 2003EL61 | 43.31 | 2000 | |
| Quaoar | 43.58 | 1290 | |
| 2003QW90 | 43.65 | 560 | |
| 1999CD158 | 43.69 | 410 | |
| 1997CS29 | 43.87 | 410 | |
| 2000CN105 | 44.65 | 430 | |
| 1998WH24 | 45.56 | 450 | |
| 2005FY9 | 45.66 | 1600 | |
| 2004PR107 | 45.75 | 520 | |
| 2003MW12 | 45.94 | 740 | |
| 2002CY248 | 46.18 | 410 | |
| 2002KW14 | 47.08 | 510 | |
| 2002AW197 | 47.30 | 940 | |
| 2002WC19 | 47.67 | 410 | |
| 2003QX113 | 49.56 | 450 | |
| 2003FY128 | 49.77 | 430 | |
| 2001UR163 | 51.40 | 620 | |
| 2002TC302 | 55.02 | 710 | |
| 1999DE9 | 55.72 | 490 | |
| 2004XR190 | 57.36 | 540 | |
| 2000YW134 | 57.77 | 430 | |
| 2003UB313 | 67.69 | 2400 | |
| 2005RM43 | 89.73 | 560 | |
| Sedna | 486.0 | 1800 | |