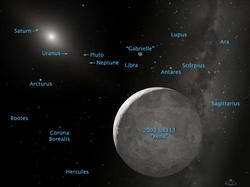
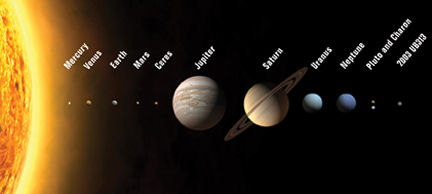
Xena
The Tenth Planet
A planet larger than Pluto has been discovered in the outlying regions of the solar system.
The planet was discovered using the Samuel Oschin Telescope at Palomar Observatory near San Diego, Calif. The discovery was announced today by planetary scientist Dr. Mike Brown of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, Calif., whose research is partly funded by NASA.
The planet is a typical member of the Kuiper belt, but its sheer size in relation to the nine known planets means that it can only be classified as a planet, Brown said. Currently about 97 times further from the sun than the Earth, the planet is the farthest-known object in the solar system, and the third brightest of the Kuiper belt objects.
"It will be visible with a telescope over the next six months and is currently almost directly overhead in the early-morning eastern sky, in the constellation Cetus," said Brown, who made the discovery with colleagues Chad Trujillo, of the Gemini Observatory in Mauna Kea, Hawaii, and David Rabinowitz, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., on January 8.
Brown, Trujillo and Rabinowitz first photographed the new planet with the 48-inch Samuel Oschin Telescope on October 31, 2003. However, the object was so far away that its motion was not detected until they reanalyzed the data in January of this year. In the last seven months, the scientists have been studying the planet to better estimate its size and its motions.
"It's definitely bigger than Pluto," said Brown, who is a professor of planetary astronomy.
Scientists can infer the size of a solar system object by its brightness, just as one can infer the size of a faraway light bulb if one knows its wattage. The reflectance of the planet is not yet known. Scientists can not yet tell how much light from the sun is reflected away, but the amount of light the planet reflects puts a lower limit on its size.
"Even if it reflected 100 percent of the light reaching it, it would still be as big as Pluto," says Brown. "I'd say it's probably one and a half times the size of Pluto, but we're not sure yet of the final size.
"We are 100 percent confident that this is the first object bigger than Pluto ever found in the outer solar system," Brown added.
The size of the planet is limited by observations using NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope, which has already proved its mettle in studying the heat of dim, faint, faraway objects such as the Kuiper-belt bodies. Because Spitzer is unable to detect the new planet, the overall diameter must be less than 2,000 miles, said Brown.
A name for the new planet has been proposed by the discoverers to the International Astronomical Union, and they are awaiting the decision of this body before announcing the name.
| object | 2003 UB313 | 2003 EL61 | 2005 FY9 |
| discoverers | Brown, Trujillo, Rabinowitz | Brown, Trujillo, Rabinowitz | Brown, Trujillo, Rabinowitz |
| size | 2400 +/- 100 km (105% Pluto) | ~3/4 Pluto | ~3/4 Pluto |
| brightness | 4th brightest Kuiper belt object (KBO) | 3rd brightest KBO | 2nd brightest KBO |
| (note that though we consider Pluto and 2003 UB313 planets, they are also clearly members of the Kuiper belt, with Pluto the brightest member) | |||
| current distance | 97 AU | 52 AU | 52 AU |
| (an AU is the distance from the earth to the sun) | |||
| orbital period | 560 years | 285 years | 307 years |
| closest approach to sun | 38 AU | 35 AU | 39 AU |
| furthest from sun | 97 AU | 52 AU | 52 AU |
| tilt of orbit compared to planets | 44 degrees | 28 degrees | 29 degrees |
| satellite? | yes! | yes! (two of them!) | no |
| surface composition | Pluto-like | water ice | Pluto-like |
| when visible | late summer, fall, early winter | later winter, spring, early summer | |